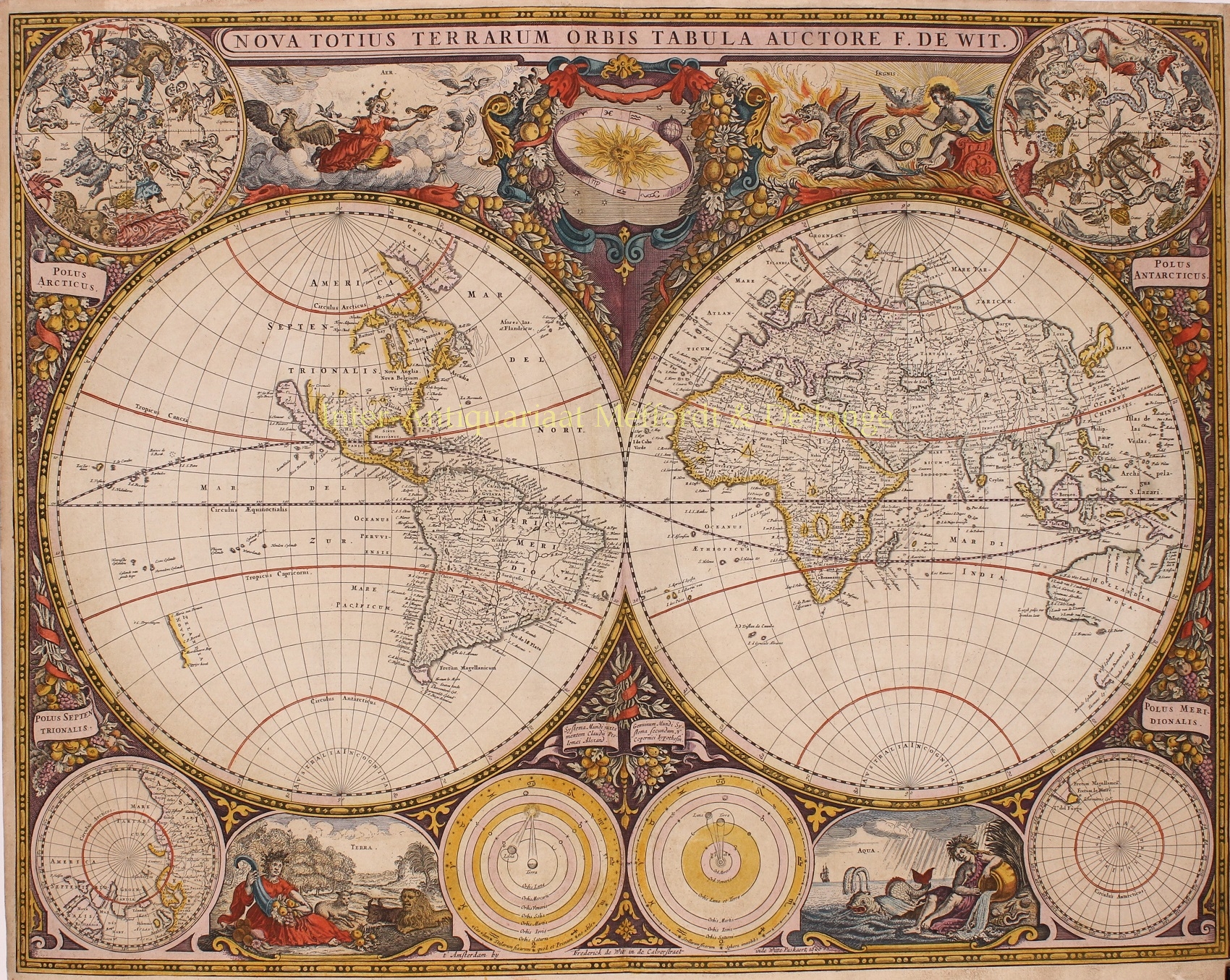
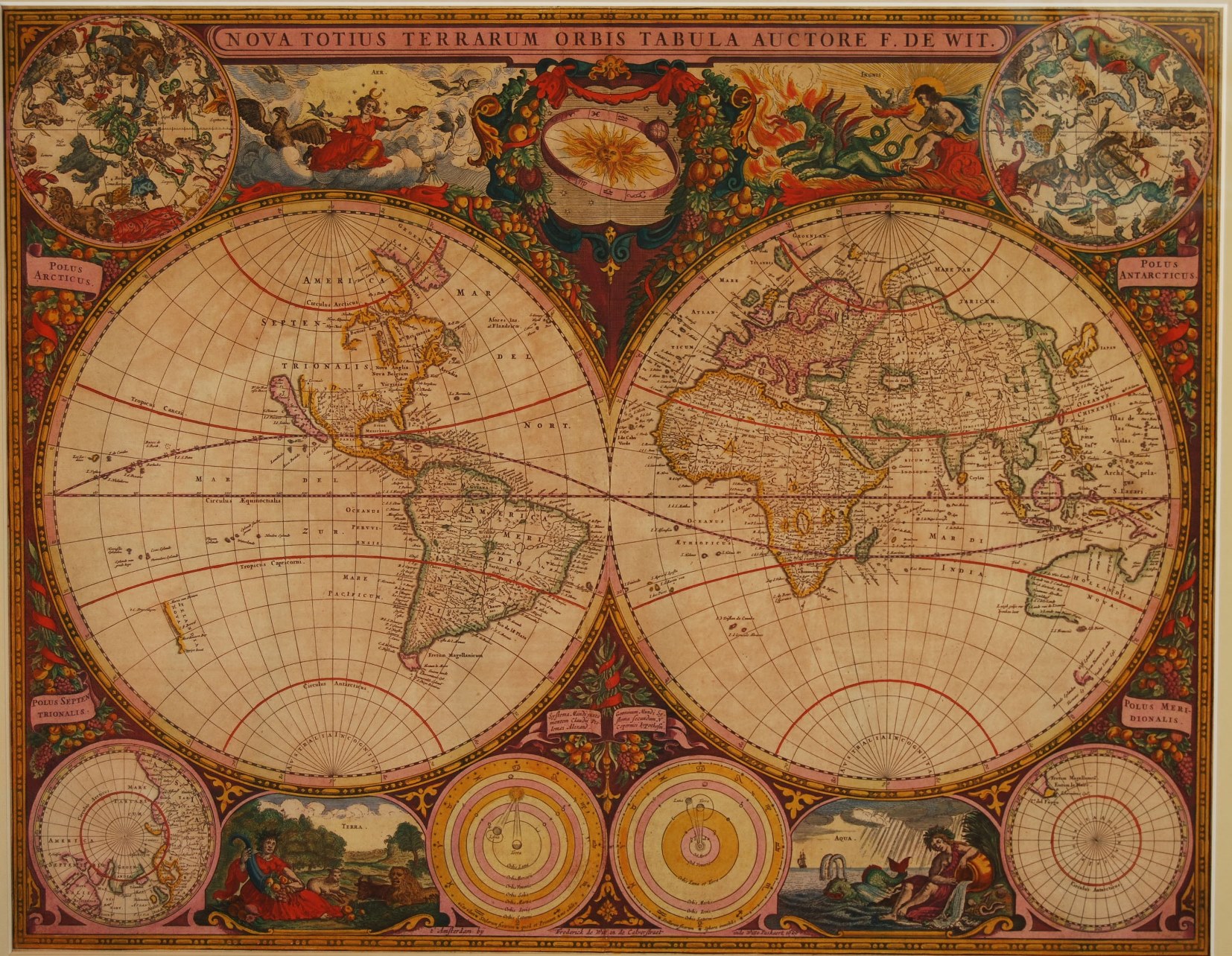
“Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula“. Copper engraving made by Frederick de Wit in Amsterdam in de Calverstraat inde Witte Pascaart in 1660. Published as part of De Wit’s Zee-Atlas Ofte Water-Wereld, or in Hendrik Doncker’s Zee-Atlas from 1660 to 1670. With original hand colouring. Size: 47 x 56 cm (plus margins).
This was De Wit’s first world map. He derived it from the two hemisphere maps from Blaeu’s wall map of 1648, reducing them in scale and making some changes. (Joan Blaeu’s own smaller world map with two hemispheres can be found here.) The upper corners contain northern and southern celestial maps and the lower corners show north and south polar projections. In the bottom center are astronomical diagrams — a geocentric one on the left and a Copernican one on the right. The top center vignette shows the sun encircled by a zodiacal ring. Between the maps and diagrams are four vignettes with allegorical depictions of the Four Elements (air, fire, earth and water). The world map also includes Baroque decorations of garlands of fruit and flowers.
A magnificent example of the art of mapmaking, this map is one of only 19 reproduced in color in Rodney Shirley’s major scholarly work on world maps of the 15th to 17th centuries. In accompanying text, the author states that “[e]specially when richly coloured, De Wit’s map is one of the most decorative standard-size maps of the time and it is much less commonly found than his three other atlas world maps.”
Frederick de Wit (1630-1706) was founder of a prominent map publishing firm in 17th century Amsterdam, the golden age of Dutch cartography. The De Wit family both published their own atlases and supplied maps to other cartographers such as Hendrik Doncker.
Reference: Rodney Shirley (1983)- “The Mapping of the World: Early Printed World Maps 1472-1700”, no. 421, plate 311.
Price: SOLD